Additive Manufacturing: Is your company up to date with what’s available and where to use it?
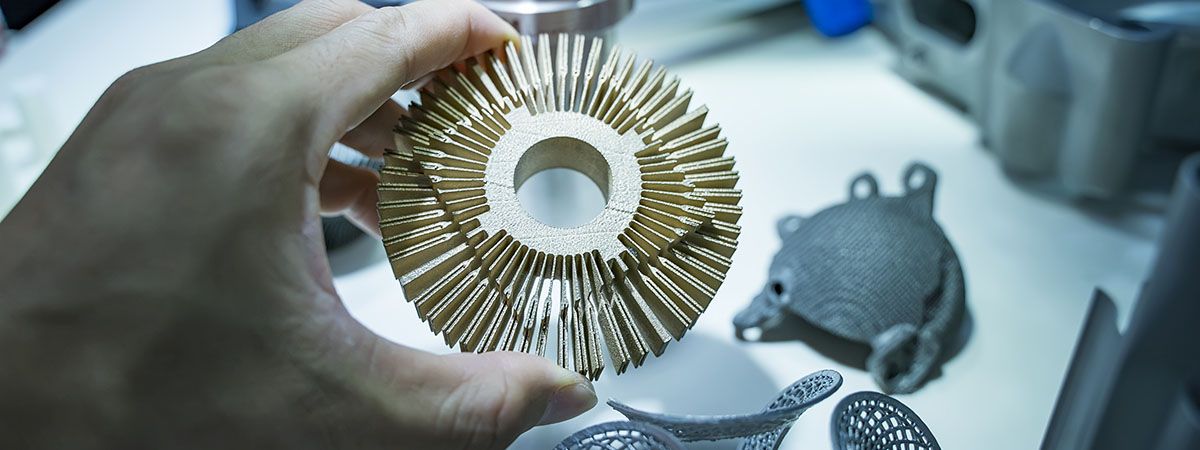
Light weighting and stiffness optimization of parts and tools, totally customized fixtures and jigs for a unique application and eradication of waste when using expensive metals and alloys. These are only few very small examples of how additive manufacturing technology is changing the way products are made in our modern manufacturing world. However, many companies only understand the tip of the ice-berg when it comes to realizing the full potential of these often-foreign ways of shaping the world around us.
Additive manufacturing technologies are becoming progressively more accessible to small and medium sized businesses, and no longer the sole domain of larger enterprises and industries. A variety of additive manufacturing technologies and applications are rapidly advancing in terms of technical capability, variety of materials available and accessibility to the smaller players in the manufacturing industry. It can sometimes be hard to keep up with what seems to be a new material or application appearing on technical websites and publications.
Functional engineering plastics are now able to be printed on smaller desktop machines and with equipment prices also dropping. Fused deposition modeling (FDM) technologies, which is the what most people think of when additive manufacturing or 3D printing is mentioned has seen a rapid growth in the types of functional materials that can now be used on smaller commercial machines.
Plastic materials such as nylon, HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene), PEI (polyetherimide), PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) are a few examples of what’s available on the market, offering a wider range of materials that can perform better under a variety of different environmental conditions. Conditions such as increased heat, stresses and corrosion performance. Small and medium companies are now able to afford their own machines to take advantage of these materials for their prototyping, tooling and production applications.
Other technologies that are perhaps not as familiar as FDM are also becoming more accessible to a wider market of eager manufactures. For example, metal printing, was not so long ago once only within reach the largest of industrial companies. Technologies such as SLM (selective laser melting), Metal Extrusion, DED (Direct Energy Deposition) and others are becoming more affordable and transitioning from proof of concept research machines to servicing a growing number of industries and applications. The boundary between new and old manufacturing methods is also being blurred, with many machines now offering post processing capabilities such as milling and other ‘all-one’ functions.
The more exotic and newer technologies also becoming within reach of smaller companies and not only in the way of purchasing the smaller machine for your workshops and factories. For those that can’t afford or don’t need to purchase their own machines, many additive manufacturing service companies are appearing around Europe making these technologies even more accessible for those looking at exploring their options or doing small one off or low volume jobs.
Yet, to many companies additive manufacturing can still seem new and a significant leap in terms of designing for and applying these technologies to existing operations. Designing processes and products for additive manufacturing is unfortunately not as simple as reading the instruction manual after purchasing a machine!
Both companies and individuals can find it hard to depart from more familiar and well-practised design principles, methods and applications suited to conventional manufacturing technologies. Companies and their managers, engineers and designers can often limit themselves and not truly reveal the enormous potential of additive manufacturing, through only looking through this accustomed lens of subtractive manufacturing.
The Advanced Manufacturing Center exists to help companies in Europe realize their full manufacturing potential. To learn more, get in touch and find out how the latest advances in additive manufacturing can be applied to your existing operations, or open entirely new product or service opportunities.
